We have been hearing a term in these last two years more than any other. It dominated the category “buzzword of the year” in 2023 and 2024. I’d doubt if it will change in 2025. But How did this concept become so buzzy that everyone, literally everyone talks about?: Artificial Intelligence or AI.
There is initially one man and one company associated with this boom of AI: Sam Altman and his OpenAI (ChatGPTs founder as you might know).
In this blog article we will discuss about the rise of AI, what AI actually is, its origin, and what differentiates traditional AI from Generative AI and beyond.
But in the upcoming articles we will dive deep into the technical side and concepts like Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Neural Networks (NN), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Prompt Engineering and so on.
All the information and ideas are based on my own knowledge, research, notes and thoughts. Since I am pretty interested in the topic and actively try to develop my knowledge and skills, throughout researches, courses, videos etc., I am exited to put these into words. Yet again, if any fact doesn’t make sense or is absurdly incorrect, feel free to reach me out and inform me about it.
The Man and The Company
First, lets talk about our main character. Samuel Harris Altman, born in 1985 in Chicago, attended to Stanford University to study computer science.
At the age of 19 he founded (or co-founded) a local social network app called Loopt. Despite it not being that successful as it one year older cousin, founded by another young entrepreneur on the other side of the country, at Harvard University (Mark Zuckerbergs Facebook.com in 2004), he managed to raise around 40 million dollars for Loopt.
Afterwards he dropped out of University after two semesters and then joined Y Combinator (a startup accelerator in Silicon Valley co-founded by Paul Graham) where he was then going to become the president.
After his YC journey he co-founded with bunch of other entrepreneurs including Elon Musk an NPO called OpenAI. YES, your read it right a NONPROFIT organization it was. ChatGPT that encourages you to pay 20$/month (or 200$ if you’d like) was intended to be free for the profit of humanity.
Well, OpenAI decided to become a for-profit organization causing Elon Musk to quit the company and mock and make accusations about OpenAI and it’s CEO.
Well this is too much bureaucracy and perhaps speculation, so lets get back to AI.
OpenAI created the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) models, starting with GPT-1 (2018), and following with GPT-2 (2019) and GPT-3 (2020). The company reached Its milestone with the release of ChatGPT in 2023 based on the GPT-3,5 model, now using GPT-4o. However OpenAI’s and so Sam Altman’s ultimate aim remains to create the AGI (Artificial General Intelligence).
After that, Google’s PaLm then Gemini, Microsoft’s Copilot, Meta’s Llama, Nvidia’s AI Chips, Perplexity, Elevenlabs, DALL-E, Sora… So many other tools, models, LLMs and startups have arisen, that made use of AI.
This is the compressed history of AI within the last eight years.
But you might ask: Wtf are all these models, LLMs, tools? How do they even work? How does AI even work? etc. In order to gain a deeper understanding, we will have to go to its foundation, to the time where all have began.
Roots Of Artificial Intelligence
Well, lets define Artificial Intelligence first: simulation of human intelligence by computer systems. (IBM Skills Network)
This idea of human-like intelligent computers wasn’t developed in recent years; it actually dates back to the 50s.
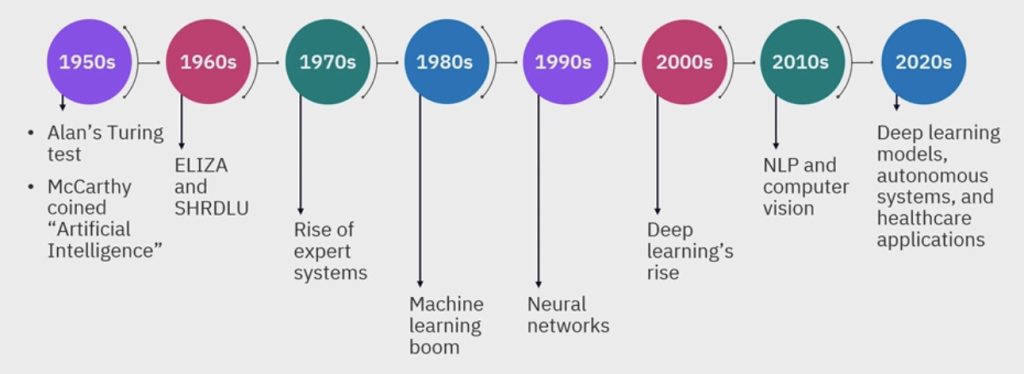
Source: IBM Skills Network
You can see the whole history of AI above. As you can tell 50s gave birth to the term Artificial Intelligence by several mathematicians and computer scientists like Alan Turing and John McCarthy. From very foundational models like ELIZA and SHRDLU in 60s to IMB DeepBlue in late 90s—the first human defeat against a computer (Garry Kasparov, world chess champion at the time lost against Deep Blue.)—from there to our Gen AI models.
So wait, what we define as AI, addressing usually ChatGPT is actually a very broad concept including many subsets and -fields. So we actually mean Generative AI, spoken of ChatGPT.
The Evolution of AI: Traditional AI vs Gen AI
Traditional AI basically analyses data and makes decisions. So its not that hard to tell that all these platforms like Youtube, Instagram, Netflix or Amazon use AI to analyze your engagement, viewed and liked content and make you recommendations or directly show appealing content according to that. They all use AI based algorithms.
On the other side Generative AI creates new content like text, image, music or video. And it doesn’t rely on pre-defined rules, instead uses deep learning techniques and rely on vast data sets, capable of using Large Language Models (LLMs) and creating content as well as human-like conversations.
While trying not to make it further complicated, lets try to clarify some terminologies with the simplest way possible:
Deep Learning analyses complex data and simulates human-making decisions.
Large Language Models (LLMs) process and generate human-like text. OpenAI’s GPT models, Googles Gemini or Meta’s Llama are all examples of LLMs.
So, Traditional AI and Generative AI have a whole different architecture.
Traditional AI
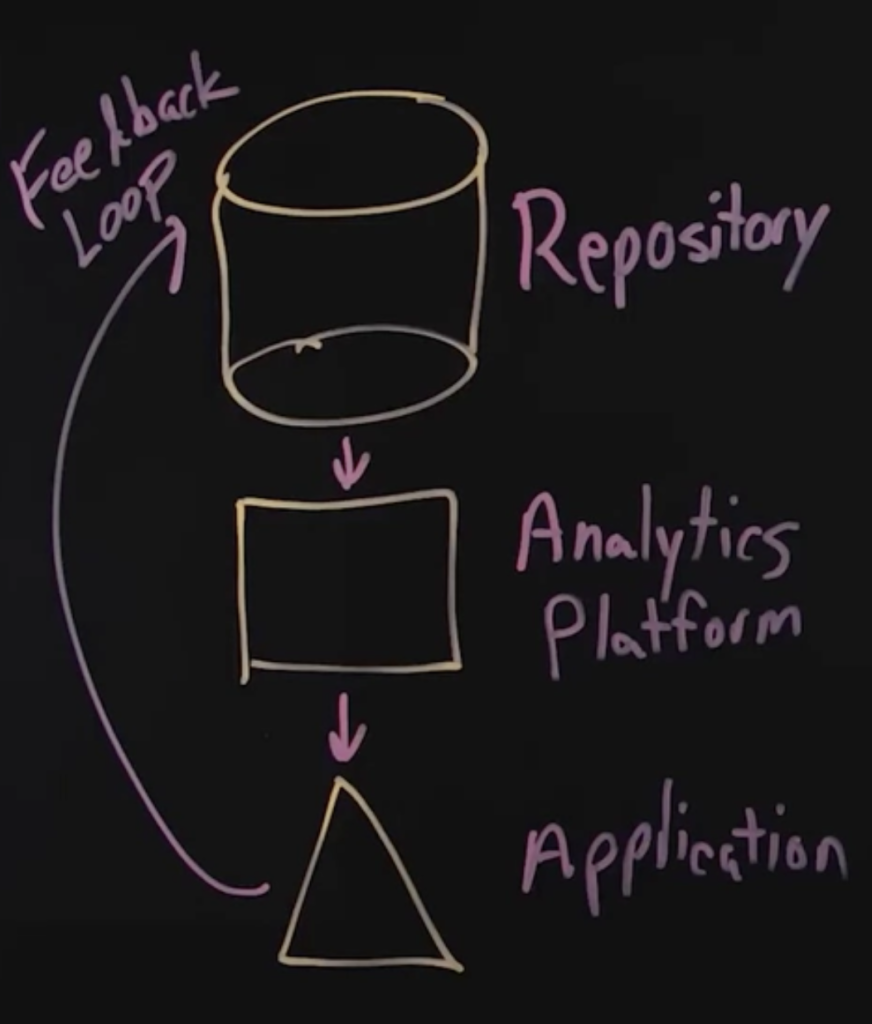
Source: IBM Technology
One of the key differences is that traditional AI, unlike Gen AI, uses the data and information that is owned by the organization, this is what Repository stands for.
The data from repository goes to the analytics platform and then the analyzed data to the application as the output. Yet this whole process isn’t an AI System unless it doesn’t learn from the application and so there is a feedback loop as a final step.
Let’s make it more relatable with an example. Let’s pick Youtube as our organization and it’s video recommendation algorithm. Youtube has a certain amount of data about you, your engagement, liked and saved videos, subscribed channels and recently viewed videos in its repository. These data are sent to the analytics platform to ideally analyze your interests and pick the most appealing content for you and then show you that interesting content as the application. Based on the videos you watch, like, save or search, the system gathers feedback, updates the repository, and refreshes your data. This is a very good example of a traditional AI system.
Generative AI

Source: IBM Technology
Generative AI relies on massive amounts of data. Unlike traditional AI, it does not depend on an organization’s internal repository but draws from publicly available, open-source data (Earth). This data is processed through large language models (LLMs) to generate outputs. However, the issue is that these outputs are often very general, as the underlying data itself is broad and not organization-specific. To address this, you refine the output using company-specific prompts (prompt tuning) before deploying it to applications. Importantly, the feedback loop does not feed back into the original data source but instead informs and improves the prompt-tuning process.
Let’s take a fictional retail company as an example. When a customer asks the company’s chatbot about its return policies, the chatbot, powered by an LLM (e.g GPT-3), initially generates a broad response based on open-source data. Using company-specific prompts, the chatbot refines this output to provide a precise answer tailored to the company’s policies. After the interaction, customer feedback (e.g., satisfaction ratings or follow-up questions) is collected and analyzed. This feedback does not update the LLM’s original training data but instead enhances the company’s prompt-tuning process, improving future responses to similar queries.
All in all, now you understand why AI has experienced a massive boom in the past two years, how OpenAI has reshaped the AI landscape, the evolution of AI throughout its history, and the key differences between traditional AI and Generative AI. I am exited to write further and share my knowledge about this topic. In the next blog article about AI, we will focus on its technical side and explore concepts like Machine Learning, Neural Networks and Natural Language Processing. Stay tuned.





